
.
“Whilst helpful in the short term – as part of the body’s healing process in response to injury or an infection – inflammation becomes harmful if it becomes chronic,” says Dr Sammie Gill, a dietitian and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) specialist.
“And it can cause damage to tissue and cause disease.”
, with its plant-based healthy fats and lean protein content, have an anti-inflammatory effect, which can be helpful in preventing and managing chronic diseases.”
Jump to:
Understanding inflammation
Chronic inflammation is low-grade (most people won’t know they have it), but persistent and can cause long-term collateral damage to tissue and organs, as well as affect immune function, leading to increased susceptibility to infections and tumours.
“Chronic inflammation can be silently damaging your body and the effects will only become noticeable over time,” says Dr Gill.
Conditions associated with chronic inflammation include:
What is the anti-inflammatory diet?
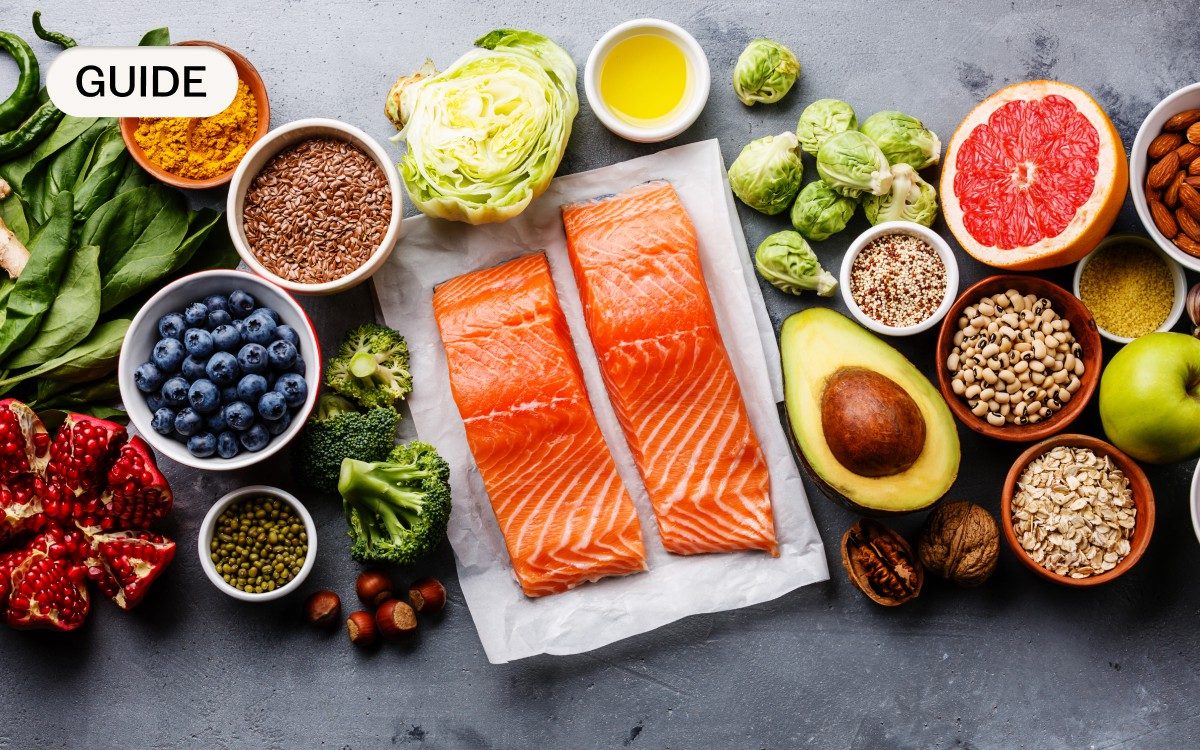
“An anti-inflammatory diet is not one diet per se, more of an umbrella term for an approach to eating a largely plant based diet, with wholegrains, legumes and lean proteins such as fish, including oily fish such as salmon and mackerel, and poultry, and only a small amount of saturated fat,” says Dr Gill.
“This approach is the foundation of the Mediterranean diet, the dietary approach to stopping hypertension (DASH) diet and the Nordic diet, which all focus on plant-based foods, healthy fats such as (oily fish, nuts and avocados), rather than red or processed meat.”
Dr Gill says diet has been shown to be a good predictor of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the blood, (high levels are a marker for inflammation in the body). “Studies have consistently shown that higher intakes for fruit, vegetables and fish are linked with lower levels of CRP. Saturated fat, red and processed meats are linked with higher CRP levels.”

) which contain palm oil.
Marcela Fiuza, a registered dietitian at Marcela Nutrition, says in her practice she uses a Med-style anti-inflammatory diet because it’s easy to follow and has the best evidence base.
“As well as metabolic health it’s very beneficial for your joints, reducing your risk of certain types of cancer, and it’s important for brain health and cognitive function. There are also benefits for your emotional health including reducing the risk of depression and improving mood.”
Foods to include
Anti-inflammatory foods include:
Foods to avoid or limit
As a general rule avoid or cut down on foods high in saturated fat and sugar.
Health benefits
.
Heart health
Most evidence for the health benefits of the anti-inflammatory diet lies in the heart health field. Going back to the 1950s, the Seven Countries Study by the American physiologist Ancel Keys found dietary patterns in the Mediterranean were associated with lower rates of heart disease and death.
) and blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides),” says Dr Gill.
Type 2 diabetes and weight management
showing improvements in glycaemic (blood sugar control).
published last year found that the Mediterranean diet was effective in helping to control blood sugar in people with Type 2 diabetes. An anti-inflammatory diet is also linked to a lower body weight and body mass index (BMI), as well as a lower risk of gaining weight over time.
Mental health
The Smiles trial found people with moderate to severe depression who followed a Med style anti-inflammatory diet, eating 50g of fibre a day, had a 32 per cent reduction in depression symptoms compared to eight per cent in a control group. Since then, other studies have reported similar findings.
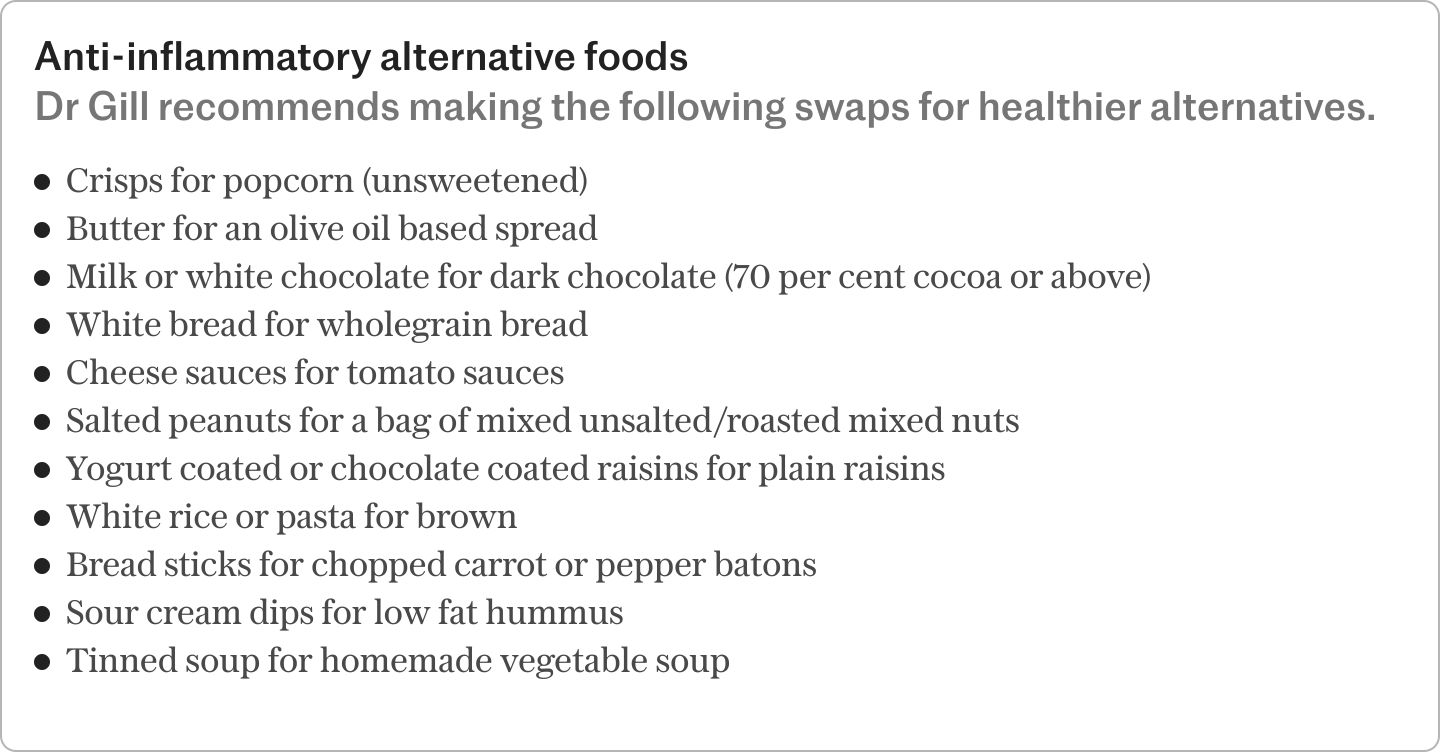
Tips for starting an anti-inflammatory diet
Compiled by Dr Sammie Gill
Recommended
Six healthy breakfasts ideas, approved by nutritionists
Read more
Play The Telegraph’s brilliant range of Puzzles - and feel brighter every day. Train your brain and boost your mood with PlusWord, the Mini Crossword, the fearsome Killer Sudoku and even the classic Cryptic Crossword.


Post a Comment
0Comments