
to make stone tools 40,000 years ago, a new study suggests.
than scientists previously thought.
discovered in the early 20th Century.
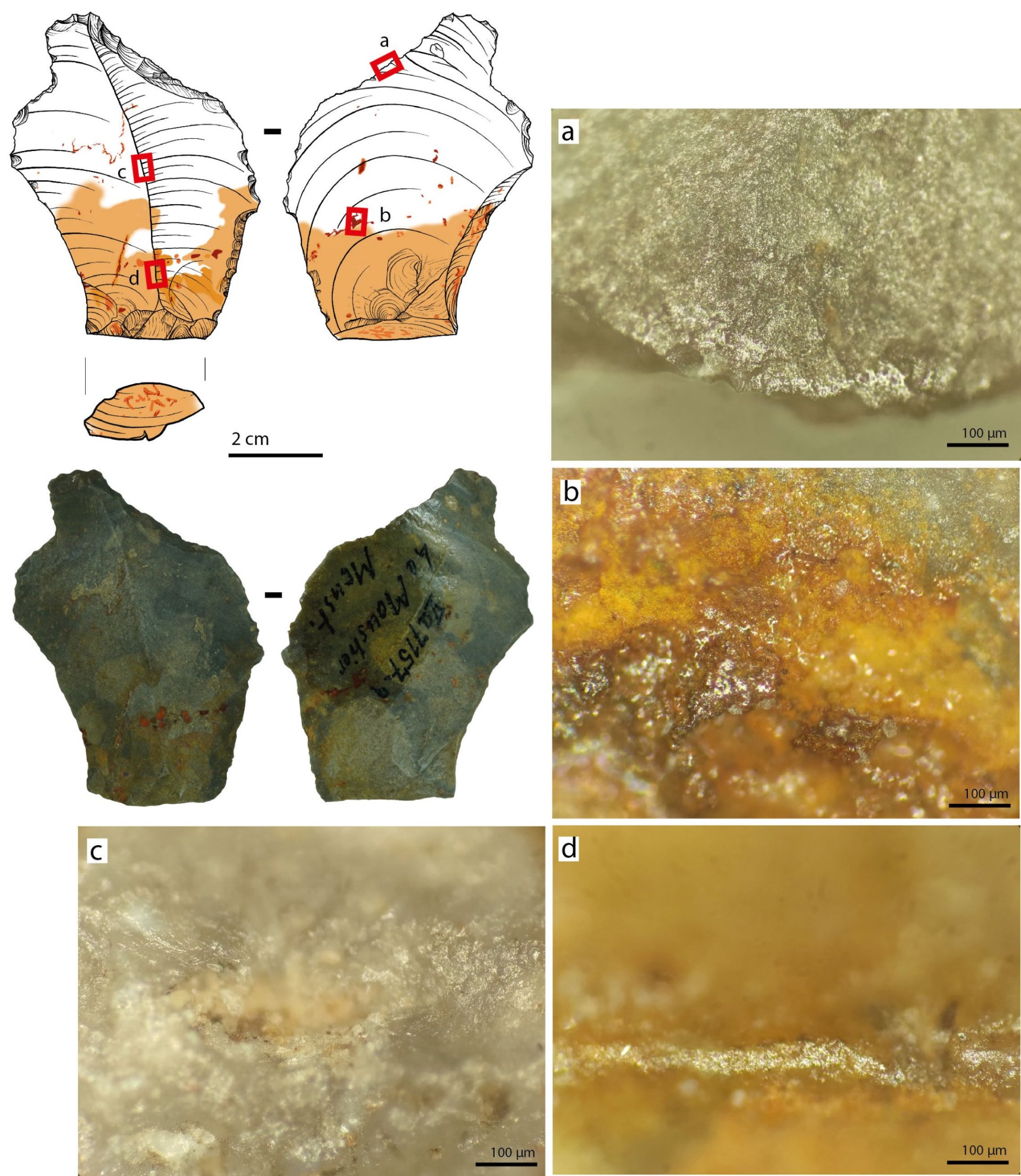
The stone tools from Le Moustier – used by Neanderthals during the Middle Palaeolithic period of the Mousterian between 120,000 and 40,000 years ago – are kept in the collection of Berlin’s Museum of Prehistory and Early History and had not previously been examined in detail.
‘The items had been individually wrapped and untouched since the 1960s,’ said Dr Ewa Dutkiewicz, of the National Museums in Berlin.
‘As a result, the adhering [sticky] remains of organic substances were very well preserved. Taking into account the overall context of the finds, we assume that this adhesive material was made by Neanderthals.’
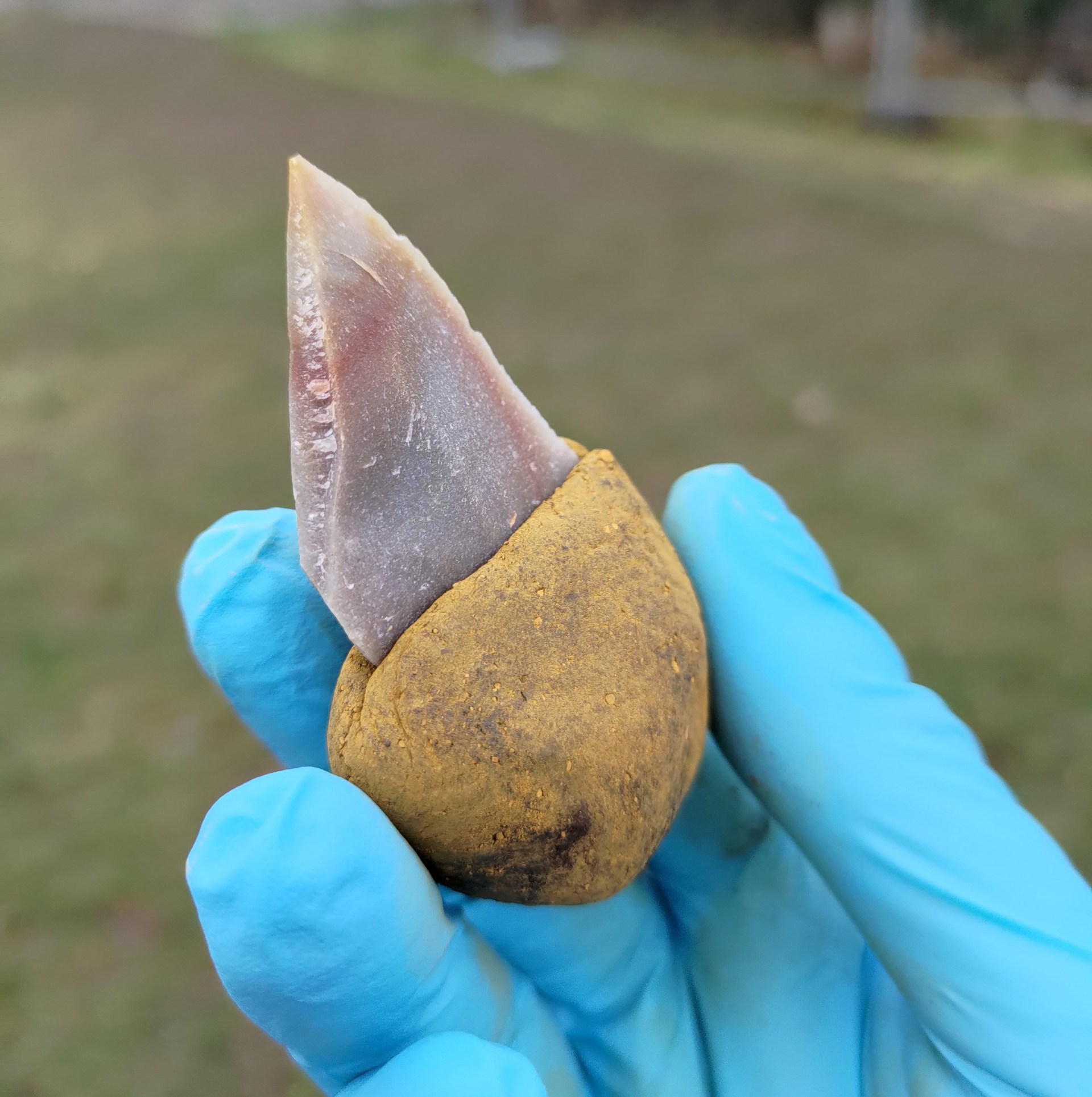

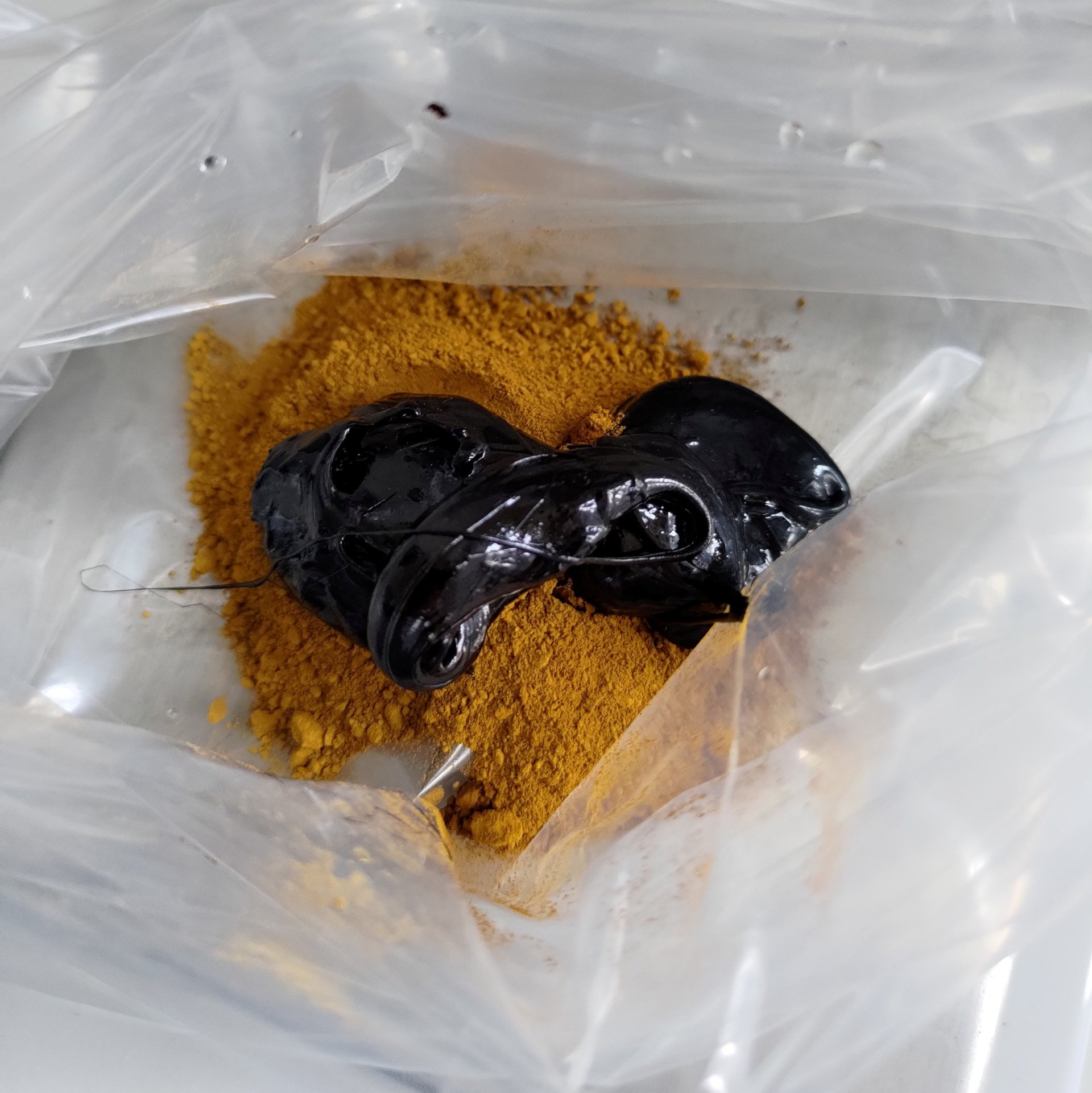
The team discovered traces of a mixture of ochre and bitumen on several stone tools, such as scrapers, flakes, and blades.
Ochre is a naturally occurring earth pigment and bitumen is a component of asphalt and can be produced from crude oil, but also occurs naturally in the soil.

The research team noted that in that particular region ochre and bitumen had to be collected from distant locations, which meant a great deal of effort, planning, and a targeted approach.
The researchers then examined these materials in tensile tests – used to determine strength – and other measures.
They found the mixture was just sticky enough for a stone tool to remain stuck in it, but without adhering to hands, making it suitable material for a handle.
In fact, a microscopic examination of the use-wear traces on these stone tools revealed that the adhesives on the tools from Le Moustier were used in this way.
The use of adhesives with several components, including various sticky substances such as tree resins and ochre, was previously known from early modern humans, Homo sapiens, in Africa but not from earlier Neanderthals in Europe.
Associate Professor Radu Iovita, of New York University said: ‘These astonishingly well-preserved tools showcase a technical solution broadly similar to examples of tools made by early modern humans in Africa, but the exact recipe reflects a Neanderthal “spin”, which is the production of grips for handheld tools.’
The researchers say that their findings, published in the journal Science Advances, present some of the best material evidence of the cultural evolution and cognitive abilities of early humans.
Adjunct Professor Patrick Schmidt, of the University of Tübingen, added: ‘Compound adhesives are considered to be among the first expressions of the modern cognitive processes that are still active today.
‘What our study shows is that early Homo sapiens in Africa and Neanderthals in Europe had similar thought patterns.
‘Their adhesive technologies have the same significance for our understanding of human evolution.’
Vivid Bulletin's News Updates newsletter


Post a Comment
0Comments